"Central banks have the power to create economic, political and social change. This is how they do it."
02 December 2014
Princes of the Yen: Central Banks and the Transformation of an Economy
06 March 2013
The Week in Economic Data: Another Non Farm Payrolls Friday
It appears as though 'trickle down' stimulus is not having its desired effect according to today's Fed Beige Book.
Fed's Beige Book Fails To Stimulate More Lending - Forbes
Jobs Report on Friday.
13 September 2012
Gold Chart: The 'Cup' Has Formed As Confidence Continues to Erode
"A moment guessed-- then back behind the Fold
Immersed in Darkness, round the Drama rolled
Which, for the pleasure of Eternity,
He doth Himself contrive, enact, behold.
But if in vain, down on the stubborn floor
Of Earth, and up to Heaven's unopening Door,
You gaze Today, while You are You-- what of
Tomorrow, when You will be You, no more?
Omar Khayyám, Rubaiyat
Today's Fed statement confirmed that QE3 is here.
After some initial hesitation the markets shot higher, believing that the Fed would do 'whatever it takes' to bring down real unemployment and to protect the financial markets.
Given that most if not all of the stimulus provided by the Fed has gone to the top percent of the economy's participants, I am struggling with what has changed that will suddenly spread the wealth to the 99 percent. The trickle down theory? Oh please.
He is monetizing the wrong debt for the wrong people in the wrong ways.
Without reform, Bernanke can print until the dollars come home to roost, before he will meet any broad employment targets in this economic structure. Unless the wealthy start hiring people to push their wheelbarrows of money to the stores.
The country needs to find a backbone and act on reform. But like Achilles, it dithers on the beach. For what reasons we may never know for certain, until history has its say.
Gold and silver took off higher like scalded cats. The charts had predicted it but I did not believe it, at least not so quickly. But there it is.
Gold has completed a 'cup' on the daily chart.
Now we would need to see a nice 'handle' to go with it.
There certainly remains the possibility that the 'cup' could fail, and gold could fall back into its broad trading range. That would be manipulation, and it could continue to work for the time being. Modern money is a funny little magician that way. I don't think we have seen anything quite like it, even in some of the more famous manias.
Bonds are the mother of bubbles. But momma swings a big stick.
Here is a look at my 'shadow' chart on gold, that I keep in background to watch developing scenarios without having to engage in unnecessarily tedious redrawing of the published chart.
The 'rim' looks to be around 1770 to 1790.
If this works, the target for this formation would be 2000+ in the next two months or so.
There are larger patterns forming on the chart that call out higher targets. As to where this ends, it ends when the economy is reformed and the median wage is healthy.
The chart situation in silver is similar, but the percentages are greater. The targets there would be roughly 43, and then 60+. This is by no means a top target.
One step at a time. In the event of a liquidity panic or exogenous event the charts may defer.
Federal Reserve Statement
Release Date: September 13, 2012
For immediate release
Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in August suggests that economic activity has continued to expand at a moderate pace in recent months. Growth in employment has been slow, and the unemployment rate remains elevated. Household spending has continued to advance, but growth in business fixed investment appears to have slowed. The housing sector has shown some further signs of improvement, albeit from a depressed level. Inflation has been subdued, although the prices of some key commodities have increased recently. Longer-term inflation expectations have remained stable.
Consistent with its statutory mandate, the Committee seeks to foster maximum employment and price stability. The Committee is concerned that, without further policy accommodation, economic growth might not be strong enough to generate sustained improvement in labor market conditions. Furthermore, strains in global financial markets continue to pose significant downside risks to the economic outlook. The Committee also anticipates that inflation over the medium term likely would run at or below its 2 percent objective.
To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee agreed today to increase policy accommodation by purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month. The Committee also will continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities as announced in June, and it is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. These actions, which together will increase the Committee’s holdings of longer-term securities by about $85 billion each month through the end of the year, should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative.
The Committee will closely monitor incoming information on economic and financial developments in coming months. If the outlook for the labor market does not improve substantially, the Committee will continue its purchases of agency mortgage-backed securities, undertake additional asset purchases, and employ its other policy tools as appropriate until such improvement is achieved in a context of price stability. In determining the size, pace, and composition of its asset purchases, the Committee will, as always, take appropriate account of the likely efficacy and costs of such purchases.
To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee also decided today to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate are likely to be warranted at least through mid-2015.
Voting for the FOMC monetary policy action were: Ben S. Bernanke, Chairman; William C. Dudley, Vice Chairman; Elizabeth A. Duke; Dennis P. Lockhart; Sandra Pianalto; Jerome H. Powell; Sarah Bloom Raskin; Jeremy C. Stein; Daniel K. Tarullo; John C. Williams; and Janet L. Yellen. Voting against the action was Jeffrey M. Lacker, who opposed additional asset purchases and preferred to omit the description of the time period over which exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate are likely to be warranted.
Statement Regarding Transactions in Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities and Treasury Securities
September 13, 2012
On September 13, 2012, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) directed the Open Market Trading Desk (the Desk) at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to begin purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS) at a pace of $40 billion per month. The FOMC also directed the Desk to continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of Treasury securities as announced in June and to maintain its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from the Federal Reserve’s holdings of agency debt and agency MBS in agency MBS.
The FOMC noted that these actions, which together will increase the Committee’s holdings of longer-term securities by about $85 billion each month through the end of the year, should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative.
Purchases of Agency MBS
The purchases of additional agency MBS will begin tomorrow, and are expected to total approximately $23 billion over the remainder of September. Going forward, details associated with the additional amount of MBS to be purchased each month will be announced on or around the last business day of the prior month.
Consistent with current practice, the planned amount of purchases associated with reinvestments of principal payments on holdings of agency securities that are anticipated to take place over each monthly period will be announced on or around the eighth business day of the prior month. The next monthly reinvestment purchase amount was also published today, and can be found here: http://www.newyorkfed.org/markets/ambs/ambs_schedule.html.
The Desk anticipates that the agency MBS purchases associated with both the additional asset purchases and the principal reinvestments will likely be concentrated in newly-issued agency MBS in the To-Be-Announced (TBA) market, although the Desk may purchase other agency MBS if market conditions warrant.
Consistent with current practices, all purchases of agency MBS will be conducted with the Federal Reserve’s primary dealers through a competitive bidding process and results will be published on the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s website. The Desk will also continue to publish transaction prices for individual operations on a monthly basis.
05 June 2012
Puzzled About QE? Watch the Adjusted Monetary Base
Quantitative easing is generally reflected in the expansion of the Monetary Base of the Federal Reserve Bank.
There could be instances wherein monetary expansion in the nature of QE could be done 'off balance sheet' in the manner of swaps, etc.
But in general, unless the monetary base starts contracting, not just stable, then QE is still in place. It can change to a form of 'qualitative easing' without affecting the overall nominal value of the base.
01 June 2012
Gold, Silver, and the May Jobs Report
"Through a set of economic policies designed to bail out and subsidize failed and often tainted corporate enterprises, while actively promoting a false sense of confidence to support those policies, the public has become exposed, by those very people entrusted to protect them, to dangerously high levels of hidden counterparty risks.
The cautionary functions of the media, the political class, and the regulatory bodies have been routinely directed, distorted, and even silenced for the benefit of a highly compromised and increasingly self-serving elite. And this corruption has begun feeding on its own momentum, resulting in increasingly blatant examples of deception, distortion, and outright theft.
This is crony capitalism, and its deadly credibility trap."
Jesse
There was a disappointment in the US Jobs Report today, and a shocking (to some) divergence between stocks and the precious metals which are staging a big rally right up now to the intermediate trendline. Although as one can see the premiums are hardly euphoric.
How come?
I looked over the Jobs numbers earlier this morning, and checked the usual suspects. Imaginary additions were 204,000 which are right 'in the groove' for the normal pattern we see for May each year.
If anything the seasonal adjustment was shaded to the downside, meaning that it would have not taken much or been out of the norm to have taken away LESS jobs in the seasonal adjustment, and brought in a report that was in line with expectations.
As an aside you remember how I feel about the histrionics around the highly volatile and revisable monthly changes versus trends. And additionally while the number of jobs is important, the median numbers and especially the median wage are the thing to watch in addition to the longer term trends.
So why put out a weak number when one could have statistically justified a stronger number? Besides 'sand-bagging' now with an eye to the second half of the year?
There are an important set of central bank decisions coming up, including the FOMC meeting shortly after the Greek elections at mid month. This weak Jobs number gives Bernanke the cards he needs to play in responding to the evolving crisis.
And you know what that means.
And this is why gold and silver diverged so hard this morning to the upside. They had been artificially pressed down for the May-June contract expirations, and some might say to lessen the impact of their rally when the inevitability of QE became evident. It also gave some of the wiseguys a great opportunity to pick up the means of production, the mining stocks, on the cheap if one is thinking longer term.
Anyone who cannot see manipulation in the precious metals markets is willfully purblind, in every sense of the word.
I am just wondering how the Feds will try and spin it. An extension of Operation Twist? The long end of the curve is approaching the ridiculous along with German and Swiss bonds. More likely there will be a swap line spun bailout of Europe, and more quietly behind the scenes, with the Jobs report for domestic cover. Perhaps the Fed will continue to expand their Balance Sheet, but not so noisily as to jawbone the economy, yet.
As I said the other day, US and Greek bonds are heading in roughly the same direction, just on different trajectories and timelines.
Gentlemen, start your presses. But try not to be too obvious about it.
01 November 2010
SP Daily Chart: US Equity Rally Reverses on SEC Probe of JPM and Magnetar CDO Issuance
The US equity market reversed its rally with the better than expected ISM number on news that JPM is under SEC investigation as reported by Bloomberg.
It appears as though JPM put together a CDO with Magnetar, which helped to select some of the components. While Magnetar bought some of the CDO, it also invested a significant amount in CDS that bet on the failure of the CDO.
The implication is that JPM and Magnetar did some of the same things that Goldman and Paulson had done.
This reversed the rally and took the financials down.
Personally I think US equities are still in their trading range with 1168 as a lower bound and 1194 as the upper bound. The wiseguys are doing a daily wash and rinse on the specs. Volumes are thin and positions are almost without any substantial foundation with the average holding time of most positions under a minute. This is a market that seems primed and ready for a flash crash, but it requires some 'trigger event' to materialize. So timing a trading decline is a bit of a fool's game in the short time.
There are three events that could affect US equities this week.
First is the national midterm election tomorrow, in which the Republicans are widely expected to take control of the House of Representatives. The Senate is a much less certain outcome. Most likely there will be 'gridlock' in the US for the next two years with power more evenly balanced between Republicans and Democrats. Any divergence from expectations in the elections results could provide some momentum out of this trading range.
The next event will be the FOMC decision on Wednesday with wide expectations of a $500 billion commitment to quantitative easing. A significant deviations from this number could provoke a market reaction.
And finally back to the real economy there will be a Non-Farm Payrolls report on Friday that will be closely watched. Consensus is for 60,000 jobs to be added.
In the background there is the 'cargo cult' of new terrorist threats permeating the news with the revelation of disguised bomb packages originating in Yemen.
This market is so artificial that it is difficult to forecast just what it will do that is out of trend.
Chart added at 4:20 PM NY Time
15 October 2010
Bill Dudley Administers QE II to Wall Street While Ben Advises (And Timmy Helps)
Pulp Fiction Adrenaline Shot
John Travolta ................ Bill Dudley, Governor, NY Fed
Eric Stoltz ..................... Ben S. Bernanke
Uma Thurman ................TBTF Wall Street Bank
Rosanna Arquette ............Timmy
Option Expiration and A Few Dates and Facts Worth Noting
As a reminder today is stock option expiration in the States.
Precious metals options expiration for November will be next week.
The US 2010 elections will be held on the first Tuesday in November which is the 2nd.
The Federal Reserve will be meeting on Wednesday 3 November, and is widely expected to be announcing a new quantitative easing program, particularly after the preface which Mr. Bernanke delivered today.
As an aside October 2010 is unusual in that it contains five full weekends, a welcome rest before the great events to come.
This is among my favorite times of the year, as the heat of summer gives way to the pleasant warm days and cool nights of autumn, and expectations of the harvest holidays and family gatherings rise, culminating in Christmas week and the beginning of a new year. The cycle of nature cares little for the comings and goings of men.
And finally, an interesting graph showing the percentage of gold as an investment in global portfolios.
09 August 2010
Trial Balloon For First Steps Toward Quant Ease 2: FT Says Fed Set to Downgrade Outlook for US
 The Federal Reserve had used Washington Post business reporter John Berry to release trial balloons ahead of its actions to gauge market sentiment and to soften any reactions to changes in their policy outlooks.
The Federal Reserve had used Washington Post business reporter John Berry to release trial balloons ahead of its actions to gauge market sentiment and to soften any reactions to changes in their policy outlooks.
Since John is no longer on the scene, have they switched to the Financial Times? This reporters speaks as though someone has already disclosed the intentions of the upcoming FOMC meeting.
This does sound like the sort of trial balloon we would expect to pre-release a change in the Fed outlook so that it does not suprise the bond markets.
Given the oversized percentage that the financial sector is taking from the real economy, like an unproductive tax on commercial business, it is unlikely that any measures will rejuvenate the US without creating another bubble.
"From 1973 to 1985, the financial sector never earned more than 16 percent of domestic corporate profits. In 1986, that figure reached 19 percent. In the 1990s, it oscillated between 21 percent and 30 percent, higher than it had ever been in the postwar period. This decade, it reached 41 percent." Simon JohnsonIt is unlikely the Fed will announce any new programs on Tuesday. That will come intra-meeting, probably after another bad round of economic news, or on some event that makes it clear that the economic "recovery" is floundering.
Financial Times
Fed set to downgrade outlook for US
By James Politi in Washington
August 8 2010
The Federal Reserve is set to downgrade its assessment of US economic prospects when it meets on Tuesday to discuss ways to reboot the flagging recovery.
Faced with weak economic data and rising fears of a double-dip recession, the Federal Open Market Committee is likely to ensure its policy is not constraining growth and to use its statement to signal greater concern about the economy. It is, however, unlikely to agree big new steps to boost growth.
Smaller measures to help the economy could initially take the form of a decision to reinvest proceeds from maturing mortgage-backed securities held by the US central bank, thereby preventing the Fed’s balance sheet from shrinking naturally.
Investors will also examine closely any changes to the pledge made by the FOMC in June to “employ its policy tools as necessary to promote economic recovery and price stability”, which could be hardened if policymakers choose to signal the potential for more aggressive move to boost the economy in the future.
But even if that happens, most economists believe that it would take several more months of poor data for the Fed to actually begin a new round of asset purchases on the scale of those carried out during the recession....
05 July 2010
Where We Are Today: Interest Rates 'Too High,' Double Dip on Deck, the Failure of Economics
David Rosenberg of Gluskin Sheff is a daily read of mine. His most recent breakfast message does a remarkably concise job of summarizing the US financial markets.
The reason for the gold market rally is obvious; declining production in the face of record monetization and increasing demand. The same financial engineers in the central banks that ruined the economy had been suppressing the price of gold through managed sales for almost thirty years in a desperate reaction to the Nixon assault on Bretton Woods in 1971. And now we see the fruits of their long contrivance, and its inevitable failure. The world will have to develop a replacement to this incredible farce we call globalization and world trade based on arbitrary and easily manipulated values.
At the same time, Dave points out that according to the Taylor Rule the Fed is overly tight, even with ZIRP! We have spoken about this in the past, in making a distinction between quantitative and qualitative easing. This also speaks to the massive deformity which the US economy had become under first Greenspan and then Bernanke, and a financial sector turned outsized predator, with little connection to real market discipline of supply and demand thanks in large part to the proliferation of derivatives.
Ben could mitigate this with the interest payments on reserves which the Fed is now allowing. I suspect at some point he will, even taking them negative if necessary. But the Fed's first priority is the insolvent Wall Street firms, and the continued charade that allows them to still pay outrageous bonuses while the nations suffers between the hammer of unemployment and the anvil of a toxic disaster in the Gulf and the collapse of its local economies. The first policy failure was in not nationalizing the insolvent US banks like Goldman and liquidating them. The second policy error is the failure to engage in serious financial reform, severely curtailing the derivatives market to something more resembling a well regulated insurance industry, and separating it completely from the commercial banking system.
It takes a certain kind of mindset and attitude to understand this dynamic, and few economists have yet taken up that challenge; economic contraction in the face of very low interest rates, with gold soaring in a bull market while long term inflation vectors are near record lows. It should be acknowledged that the Fed is active in the markets, 'tinkering' with the longer end of the yield curve among other things. And of course, derivatives, easily printed and without position limits, are pressed on various targets in the real economy almost at will by the banks and hedge funds, distorting prices and markets, destroying real wealth. And yet this is what we have, facts in collision with theories. The austerity reaction in Europe is the resurrection of Hoover, of the liquidationism which drove the US into the agony of the trough of the Great Depression of 1933. This was of course the moment of failure for the Austrian School. It is one thing to be able to spot a problem and to stop it ahead of time, which their theories do well. But the Austrians seemed unable then, and now, to recommend practical and implementable programs to remedy the current situation in which the US now finds itself.
And yet this is what we have, facts in collision with theories. The austerity reaction in Europe is the resurrection of Hoover, of the liquidationism which drove the US into the agony of the trough of the Great Depression of 1933. This was of course the moment of failure for the Austrian School. It is one thing to be able to spot a problem and to stop it ahead of time, which their theories do well. But the Austrians seemed unable then, and now, to recommend practical and implementable programs to remedy the current situation in which the US now finds itself.
This is not to say the theory has failed, but rather that it has intellectual arteriosclerosis and atrophy. It is one thing to read and write about riding a bicycle or having sex; it is another thing to get out of your rooms and do it, and actually learn something. To their credit they were certainly not fooled by the neo-liberals. But their response is little better than the neo-Keynesians, which is to reflexively stimulate or liquidate without practical reforms and actually fixing the distortions which policy errors over a long period of time have caused.
I have to admit that I like to tweak the nose of 'the Austrian school' now and then. But since I tend to hit the neo-liberals with brass knuckles, and the neo-Keynesians with the kind of premeditated distance one gives to a crotchety old maiden aunt dwindling into senility, I would hope they understand that it is not personal; all of the modern schools of economic thought have failed. All of them, for varying reasons. That is all well and good and human, but it is the lack of recognition of that failure, and the resolution to adapt and do better, and to roll up one's sleeves and actually shame the politicians into doing better for the people, that is so cloying.
The failure of economists in general to speak out, except in the usual sniping reminiscent of departmental politics, is leaving the field open to quackery, and the draconian measures of oligarchy. Just as their failure to speak out permitted China to distort the world economy, and Greenspan to destroy the economic infrastructure of the US.
The current economic landscape seems littered with self serving cronyism, broken theories disconnected from reality, quackery, and obtuse boasting from dismal failures. Economics seems more like astrology, or Elliot Wave theory, or the writings of Nostradamus, with so little rigor that it can be used to 'prove' or justify just about any outcome, after it has happened. In short, economics seems these days to be little more than propaganda, social commentary rather than harder science or something as simply practical as mechanical engineering.
What I am saying is that all the economic schools of thought have come up short, failing badly, the free market neo-liberals most spectacularly of all. Their failure is not in having got it wrong, but in continuing to beat the dead horses of their theories until the stench is unbearable.
The lack of significant financial reform, and restraint of unbridled speculation through the use of derivatives, is going to strangle the western world until they can bring themselves to restrain their banking system gone mad.
The U.S. turned 234 years old yesterday, and yet over half of the nation’s money supply was created since Helicopter Ben took over the flight controls four years ago.
No wonder gold is in a full fledged bull market. The annual output of gold has declined 12% in the past decade while the marginal cost has more than doubled, to $500, according to David Hale. Moreover, David points out in his recent report that since 1900, more than 80% of the world’s proven reserves have ready been mined.
The marginal cost of pressing on Dr. Bernanke’s printing machine is basically zero, and, the prospects of a re-expansion of QE by the Fed as double-dip risks rise with each and every passing data-point are rather high.
Gold has corrected to the 50-day moving average in recent weeks, which in the past has been a terrific entry point — for the past six months, each low has been higher and each high has been higher too. Nice upward channel that is to be respected and to be bought.
As for double dip risks, the ECRI leading index is predicting over 50-50 odds of such, and is exactly where it was in December 2007 when unbeknownst to the vast majority at the time that the downturn was just getting started.
As an aside, even after cutting his growth forecast on Friday, Bank of America’s chief economist went on CNBC after the market closed and declared that the economy would manage to “muddle through” — this has now become the widespread consensus that all this is nothing more than a temporary soft patch. [akin to quicksand, an economic netherworld such as that which the kereitsu inflicted on the people of Japan - Jesse]
Jeffrey Frankel, a member of the NBER’s business cycle committee, had this to say over the weekend:“You cannot rule out a double dip, in light of Europe’s problems … I think the next couple of months of indicators will be more telling than the last couple of months.”Economists have spent so much time trying to assess when the last recession ended that they have taken the eye off the ball as to when the next one would begin. Yet this is what the NBER is grappling with — maybe the same day the NBER announces that the last recession ended in June 2009, they will tell us that another one began in June 2010.
Can a sub 3% yield on the 10-year note and the “flattest” Treasury curve (still near 230bps, mind you, for the 2s/10s spread) in nine months really be sending out the wrong message of heightened hard-landing risks? Or, for that matter, the lowest close in the S&P 500 since September 4th of last year. Did anyone back then think we would go from Labour Day to Independence Day with nothing to show for it?"
...What does not get enough play is that Fed policy is tighter than it should be right now, based on the Taylor Rule, believe it or not — zero policy rate and the size of the Fed’s balance sheet is equivalent to a -2% rate, when at this stage the two tools should be equivalent to a -5% rate. [We might have an effective negative rate if the government had not fouled the measures of inflation - Jesse] And, fiscal policy is actually far less stimulative than meets the eye when the impact of State/local government restraint is factored into the equation. In the past two months, whether one looks at the Kansas City or St. Louis Fed’s stress indices, there have been 60 basis points of tightening in overall financial conditions, just as the economy is hitting a possible inflection point.
David Rosenberg, Gluskin Sheff, Breakfast with Dave
A double dip recession will be a strong indication, if not a proof, of policy error, both on the part of the Federal Reserve and of the Obama Economic Team. When the recession can no longer be hidden from the public the reaction could be swift. The oligarchs are acting pre-emptively to cushion the blow on their ill gotten gains by preaching austerity measures, at a time when the lower and middle classes are taking it on the chin. Empathy and common sense have little place with obsessive sociopaths
Part of the problem is the China peg to the US dollar. This obviously thwarts the international market's system of checks and balances, its ability to adjust naturally to changes in economic fortunes. That peg and devaluation ought never have been allowed.
But this is merely one instance in a series of economic manipulations and sometimes aggressive deceptions by the world powers that have been occurring since 1971, when Nixon unilaterally broke the Bretton Woods regime and took down the international gold standard, and not incidentally brought Greenspan into the service of the federal government.
Reform is the only solution that is sustainable. Austerity or stimulus without reform are worse than useless. One does not fix a car with a blown engine by flooding it with gasoline, since it did not run out of gas, but in fact blew up from prolonged abuses and disrepair. And on the other hand, one cannot restart the economy by watching it burn, waiting for the flames to extinguish themselves, hoping for a chance to start over anew and do it 'the right way' according to theory. By the time you would wish to get started, there will have been a revolution conducted by the impatient and long suffering people. So what does one do?
You fix it. You restore it to a state when it was last actually working, and resist the temptation to 'optimize' and redesign it on the fly, cramming in pet projects that surpass performance tweaks. That can come later, after the system is running again in some reasonable way. You take the harder hits when they can be absorbed with toppling the recovery.
That is how it is. Everything else is noise, excuses, partisanship, and waffling.
26 January 2010
Quantitative Easing: We Are All Central Planners Now
"What does the Fed think will change if they can avert a crash again and maintain the status quo at the cost of yet another asset bubble?
Is the Fed trying to maintain an inherently unstable economic order that requires increasingly extraordinary means and ever greater imbalances to keep it from collapsing? I believe that they are.
Will the Fed have to keep assuming more and more power and control over the real economy to sustain the unsustainable until they destroy what they had intended to save? I think the answer is yes."
Quantitative easing effectively means providing the financial system with liquidity well in excess of organic commercial demands and conventional open market operations. The Fed does this by expanding its balance sheet extraordinarily, hence the spectacular growth in 'excess reserves' of commercial banks.
The Fed does this for several reasons. The first obviously is to supply reserve capacity to the banks when their own reserve base has deteriorated badly to the point of insolvency. A second reason is to permit the Fed to expand its Balance Sheet in an extraordinary manner, in order to absorb assets that cannot be marked to market by a commercial bank without significantly damaging their own balance sheet. A third reason of course is to take an accommodative stance with regard to real interest rates when nominal rates approach zero.
One of the issues that quantitative easing creates is that it is problematic to continue to effect a fed funds rate. The usual method is to set a target, and then make changes in the levels of liquidity in the system through adds and drains of financial assets like Treasuries to achieve it. This is why Fed Funds is called a 'target rate.'
But how can one do this when the tool of policy making has been thrown in a ditch by the adoption of quantitative easing, by definition driving rates to zero? It is all "adds" and no drains, stuffing the goose beyond its capacity as it were.
Make no mistake: quantitative easing is to central banking what the introduction of nitroglycerin was to conventional warfare. It kicks the power of financial engineering up a notch, to say the least, and brings in an element of risk of more than normal inflationary pressures.
The Fed can set a 'floor' under the overnight interest rate without engaging in open market operations by offering to take reserves and pay a set rate as interest. Presumably banks will take a riskless .25% rather than place funds in the markets at something lower than this. And they will not achieve a higher return for a commensurate risk because the system is awash with liquidity, and prospective borrowers are surrounded by the hidden shoals of marked to model.
This works in the first wave of quantitative easing. But what happens when the Fed seeks to add additional tranches of funds through market purchases of even more dodgy assets, or even begin to exercise more control over the banking system as the economy recovers to avoid a hyperinflation? "Draining" through open market operations is not easy if the banking system is still more fragile than its nominal balance sheets would suggest. In a sort of Gresham's Law, the banks wish to hoard the Treasuries, and disburse their collateralized bundles. Pulling out Treasuries removes the core of their assets.
 The Fed is now seeking a 'deposit rate' which in addition to its 'overnight rate' would commit banks to place funds with the Fed for a set period of time, in the manner of a certificate of deposit rather than a demand account.
The Fed is now seeking a 'deposit rate' which in addition to its 'overnight rate' would commit banks to place funds with the Fed for a set period of time, in the manner of a certificate of deposit rather than a demand account.This article from Bloomberg is an indirect pre-announcement from the Fed that they may abandon the notion of 'target rates' altogether, and set interest rates by fiat, rather than achieving them in the marketplace by adjusting levels of short term liquidity. This marks a transition from 'Phase I' to 'Phase II' of Bernanke's monetary experiment.
I want to emphasize the significance of this change.
This is becoming a pure 'command and control' economic financial engineering by the Fed, in which it sets rates by its decision, without engaging in market operations which could encounter headwinds against those policy decisions. It is similar in magnitude to the Fed monetizing Treasuries directly without subjecting interest rates to the direct discipline of the market. This is of a pedigree more in keeping with a command and control Five Year Plan than a market economy. Extraordinary times call for extraordinary measures the Fed and its apologists might say.
I do not wish to overstate this, but it also suggests that a continuation of the Fed's open market purchases would place an excessive strain on its own balance sheet, which has a much lower percentage of Treasuries than at most times in its history. One would have to wonder if the Fed itself could pass a stress test or a serious audit of the quality of its stated assets.
It is less costly for the Fed to pay interest directly on bank deposits and just set the rate, especially if they are in the form of time defined certificates of deposit, than if it were to continue buying up decaying financial assets to achieve its goals.
In a sense, the Fed is competing with commercial enterprise in 'borrowing' from the banks for its own balance sheet, to affect its policy measures. This is what is meant by setting a floor under the short term rates.
As an aside, I found this quote in the Bloomberg article quite to this point:
"By raising the deposit rate, now at 0.25 percent, officials reckon banks will keep money at the Fed and not stoke inflation by lending out too much as the economy recovers."
The level of reserves they are holding and the rate which they return through their interest program are being used to throttle lending to the commercial companies at market clearing rates. Granted this is all a part of a more aggressive and complex implementation of interest rate policy, but it presents a new level of financial engineering and explicit control of money flows that is quite likely corrosive to a market system, and fraught with unintended consequences.
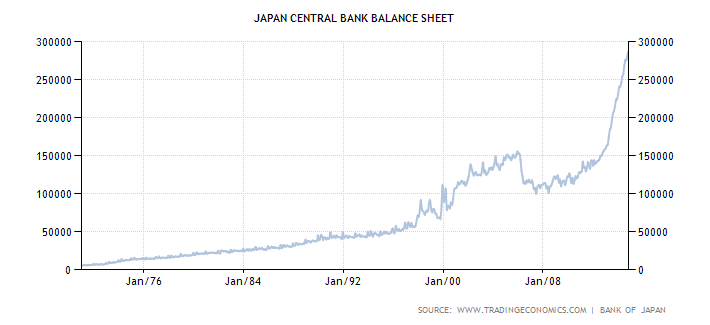
The US Federal Reserve did not originate the concept of quantitative easing. It began with the Japanese central bank, which one might uncharitably say erred on the side of supporting the banks and the corporate conglomerates, and drove the economy into a protracted slump. There were, we should add, significant mitigating factors including the Japanese demographics and penchant for high savings at low rates in the government postal system.
This is an 'experiment' on the part of the UK and US in their own go at quantitative easing. The risk is obviously inflation, and they are seeking to downplay that at every turn. It is the perception of inflation that the Fed will seek to quell, as it continues to adjust the money supply in ways and with tools that it thinks it understands, but which it has never used before. Perception of inflation is their greatest fear. Once it takes hold it is difficult to stop.
One has to wonder what the anticipated endgame might be. A global currency regime with comprehensive central planning? Since 1999 the financial engineers at the Fed have been unable to achieve sustainable growth in the US national economy as is it is now constituted without generating asset bubbles through abnormally low interest rates. As recovery goes the last was anemic in terms of jobs growth, and this latest effort appears to be even more fruitless.
What does the Fed think will change if they can avert a crash again and maintain the status quo at the cost of yet another asset bubble?
Is the Fed trying to maintain an inherently unstable economic order that requires increasingly extraordinary means and ever greater imbalances to keep it from collapsing? I believe that they are.
Will the Fed have to keep assuming more and more power and control over the real economy to sustain the unsustainable until they destroy what they had intended to save? I think the answer is yes.
Bloomberg
Fed Weighs Interest on Reserves as New Benchmark Rate
By Scott Lanman
Jan. 26 (Bloomberg) -- Federal Reserve policy makers are considering adopting a new benchmark interest rate to replace the one they’ve used for the last two decades.
The central bank has been unable to control the federal funds rate since the September 2008 bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc., when it began flooding financial markets with $1 trillion to prevent the economy from collapsing. Officials, who start a two-day meeting today, have said they may replace or supplement the fed funds rate with interest paid on excess bank reserves.
“One option you might want to consider is that our policy rate is the interest rate on excess reserves and we let the fed funds rate trade with some spread to that,” Richmond Fed President Jeffrey Lacker told reporters on Jan. 8 in Linthicum, Maryland.
The central bank needs to have an effective policy rate in place when it starts to raise interest rates from record lows to keep inflation in check, said Marvin Goodfriend, a former Fed economist. Policy makers are concerned that the Fed funds rate, at which banks borrow from each other in the overnight market, may fail to meet the new target, damaging their credibility and their ability to control inflation as the economy recovers.
‘Extended Period’
The choice of a benchmark is the “front line of defense against inflation, and also it’s at the heart of the central bank being able to precisely and flexibly guide interest-rate policy in the recovery,” said Goodfriend, now a professor at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh.
The Federal Open Market Committee is likely to maintain its pledge to keep interest rates “exceptionally low” for an “extended period” in a statement at about 2:15 p.m. tomorrow, economists said. The Fed probably won’t raise interest rates from record lows until the November meeting, according to the median of 51 forecasts in a Bloomberg survey of economists this month.
Fed Chairman Ben S. Bernanke, in July Congressional testimony, called interest on reserves “perhaps the most important” tool for tightening credit.
Inflation Concerns
Banks’ excess reserves, or deposits held with the Fed above required amounts, totaled $1 trillion in the two weeks ended Jan. 13, compared with $2.2 billion at the start of 2007. The Fed created the reserves through emergency loans and a $1.7 trillion purchase program of mortgage-backed securities, federal agency and Treasury debt.
By raising the deposit rate, now at 0.25 percent, officials reckon banks will keep money at the Fed and not stoke inflation by lending out too much as the economy recovers.
The new policy may be similar to what the Bank of England does now, said Philip Shaw, chief economist at Investec Securities in London. The U.K. central bank’s benchmark interest rate, now at 0.5 percent, is the rate it pays on the reserves it holds for commercial banks. It may drain excess liquidity from the system by selling back the gilts it has purchased through its so-called quantitative easing program, Shaw said.
Communications Strategy
Policy makers will need to adopt a communications strategy to explain the new benchmark because “people might have had a hard time getting their mind around the idea that the official rate had become the interest on reserves rate,” said Kenneth Kuttner, a former Fed economist who has co-written research with Bernanke and now teaches at Williams College in Williamstown, Massachusetts.
Without a federal funds target, banks might have to find a new way to set the prime borrowing rate, the figure most familiar to consumers that that is now pegged at three percentage points above the fed funds target.
In the past, the Fed had controlled the rate by buying or selling Treasury securities, adding or withdrawing cash from the system. That mechanism broke down when the Fed started flooding the system with cash after the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers to prevent a financial meltdown.
The deposit rate would help set a floor under the fed funds rate because the Fed would lock up funds by offering a fixed rate of interest for a defined period and prohibiting early withdrawals.
‘Risk Free’
“In general, banks will not lend funds in the money market at an interest rate lower than the rate they can earn risk-free at the Federal Reserve,” Bernanke said in an October speech in Washington.
The New York Fed has been testing another tool, reverse repurchase agreements, as a way of pulling cash out of the financial system. In that case, the Fed would sell securities and buy them back at an agreed-upon later date.
There could be complications to using the deposit rate. Banks may be able to generate more revenue by lending at prime rate rather than by earning interest at the Fed, said William Ford, a former Atlanta Fed president at Middle Tennessee State University in Murfreesboro.
Also, the Fed’s direct control over a policy rate --instead of targeting a market rate -- could skew trading and financing toward short-term borrowing once investors know the rate won’t change between Fed meetings, said Vincent Reinhart, a former Fed monetary-affairs director.
The new reliance on reserve interest could also increase the policy clout of Fed governors in Washington at the expense of the 12 regional Fed bank presidents, Reinhart said.
Congress gave only the Fed governors the authority to set the deposit rate. The presidents have historically favored higher rates and voiced more concern about inflation.
“The Federal Reserve Act puts a very high weight on comity,” said Reinhart, now a resident scholar at the American Enterprise Institute in Washington. Using interest on reserves for setting policy “can change the tenor of the discussions, and I don’t know how they get around it.”
22 December 2009
Quantitative Easing: the Opiate of the Banks
Much is being made of Bernanke's program of quantitative easing, which is nothing more than an extreme form of artificially low rates of interest with direct monetization of debt in the aftermath of a financial crisis.
The current program of quantitative easing is not only no miracle cure, it will not work at all, will not 'fix' the problems that are plaguing the American economy in any substantial manner. It is a misguided subsidy and reinforcement of reckless behaviour, and a corrupt distribution of wealth.
Quantitative easing would only be a cure if the crisis had been caused by an exogenous credit shock, a sudden withdrawal of liquidity due to an event unrelated to the workings of the domestic economy like a war or an act of nature.
But this is clearly not the case. For the cause of the financial crisis was in fact a lengthy period of artificially low interest rates under the chairmanship of Alan Greenspan, which allowed all manner of financial excess and malinvestment and even fraud to fester in the real economy for a protracted period of time until it became embedded, and one might even say a dominant force, in the economy. It warped and distorted the productive economy.
Applying quantitative easing may relieve the symptoms of the credit crisis but it is merely a palliative, not a cure. It is similar to the case of a debilitated addict who, being denied his marcotics, goes into shock and suffers a heart attack. Yes, a 'fix' of the drug of choice will relieve the short term symptoms perhaps, but will do nothing for the underlying state of health which will continue to worsen.
The very low rates of interest have 'cured' the short term credit seizure in the financial markets, thereby providing time and opportunity to engage in genuine systemic reform and rebalancing to repair the distortions that caused the crisis in the first place: an outsized and corrupt financial sector, and a system of global trade that is freakishly imbalanced and manipulated by command economies and multinational corporations. That, and a lapse of western governance overcome by greed.
Until those reforms are made, the US economy will experience a series of bubbles and crises that, through the US dollar reserve currency system, will shake the governments of the world to their foundations.
19 November 2009
Short Term T Bills Go Negative
Too many dollars chasing too few opportunities because of mispriced risk, so they are piling into short Term Treasuries again.
Grab something solid and hold on tight. Could be rough seas ahead.
Three Month T Bill Rates Go Negative On Concern Risk Rally Overdone
By Cordell Eddings
Nov. 19 (Bloomberg) -- Treasury three-month bill rates turned negative for the first time since financial markets froze last year on concern that the rally in higher-yielding assets has outpaced the prospects for economic growth.
Investors were willing to pay the government to hold their money as stocks slid amid speculation the eight-month, 68 percent rally that drove the valuation of the MSCI World Index to the most expensive level in seven years already reflects forecasts for a 25 percent rebound in corporate earnings next year. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis President James Bullard yesterday said experience indicates policy makers may not start to increase interest rates until early 2012.
“As long as the economy is stuck in a rut and there are not viable fixed-income alternatives, they will buy Treasuries,” said George Goncalves, chief fixed-income rates strategist at Cantor Fitzgerald LP, one of 18 primary dealers that trade directly with the Fed.
Rates turned negative on some bills maturing in January, according to Sarah Sobeck, a Treasury trader at primary dealer Jefferies & Co. The three-month bill rate was at 0.0051 percent, the least this year. Six-month bill rates dropped to the lowest since 1958. Treasury bills turned negative last December for the first time since the government began selling them in 1929 as investors scrambled to preserve principal and were willing to sacrifice returns in the months following the collapse of Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc.
The two-year note yield fell five basis points to 0.70 percent at 4:24 p.m. in New York, according to BGCantor Market Data. The 1 percent security due October 2011 rose 3/32, or 94 cents per $1,000 face amount, to 100 18/32. The yield touched 0.6759, the lowest since Dec. 19. It fell to an all-time low of 0.6044 percent on Dec. 17.
Don’t Dismiss
“Investors are preparing early for year-end and trying to ensure liquidity,” said Sobeck. “The move in the two-year resulted from the bid for collateral.”
Banks typically buy the safest maturities at the end of the year to improve the quality of assets on their balance-sheets.
Two-year yields rose yesterday following the comments from Bullard, who will be a voting member of the Federal Open Market Committee next year.
“The fact that he introduced the idea should not be dismissed as the ranting of a madman,” according to a report by senior economist Tom Porcelli and interest-rate strategist Christian Cooper at primary dealer RBC Capital Markets in New York. “Even the most bearish analysts weren’t talking about 2012 as a possibility. But the idea has just received credibility.”
Bullard’s comments followed a Nov. 16 speech by Fed Chairman Ben S. Bernanke in which he indicated that the central bank’s extended period of low borrowing costs may be even longer amid economic “headwinds.”
New Asset Bubbles
Bill Gross, who runs the world’s biggest bond fund at Pacific Investment Management Co., said the “systemic risk” of new asset bubbles is rising with the Fed keeping interest rates at record lows.
“The Fed is trying to reflate the U.S. economy,” Gross wrote in his December investment outlook posted on the Newport Beach, California-based company’s Web site today. “The process of reflation involves lowering short-term rates to such a painful level that investors are forced or enticed to term out their short-term cash into higher-risk bonds or stocks.”
The central bank lowered its target rate to a range of zero to 0.25 percent in December and purchased $300 billion of Treasuries this year as part of its effort to lower consumer borrowing costs and support the housing market, the collapse of which triggered the worst slump since the Great Depression....
25 September 2009
Do Ben and Tim = Thelma and Louise?
One cannot help but note that Team Obama is trying to derail serious proposals regarding financial reform for Wall Street at the G20 meeting, as we suggested they would.
The concerns raised by US revelations at the G20 today about new intelligence regarding Iran's secret underground nuclear facility have overshadowed financial reform and economic problems, and Gordon Brown's prescription yesterday that the G20 would become the new governing council for the world. It also stepped rather heavily on the House Hearings on HR 1207 "Audit the Fed" bill sponsored by Ron Paul and a good part of the Congress.
Why waste a crisis indeed. Especially when you can cop a two-fer.Yesterday we put forward a somewhat lengthy piece on the Fed and reverse repos being considered titled Fed Eyes US Money Market Funds.
There is a key quote in there that we would like to highlight today.
The central bank is now considering dealing with money market funds because it does not think the primary dealers have the balance sheet capacity to provide more than about $100 billion... Money market mutual funds have about $2.5 trillion under management..."Only 100 billion in available capital for a relatively risk free short term investment in the global banking system including the Primary Dealers, does seem a bit tight for a set of such 'well capitalized' banks, especially since they aren't making many commerical loans, preferring to speculate in the commodity and equity markets for daytrading profits.
BNP Paribas Securities Corp., Banc of America Securities LLC, Barclays Capital Inc., Cantor Fitzgerald & Co., Citigroup Global Markets Inc., Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC, Daiwa Securities America Inc., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., Goldman, Sachs & Co., HSBC Securities (USA) Inc. , Jefferies & Company, Inc., J. P. Morgan Securities Inc., Mizuho Securities USA, Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated, Nomura Securities International, Inc., RBC Capital Markets Corporation, RBS Securities Inc., UBS SecuritiesLLC.
Couple that with the revelation reported some time ago at ZeroHedge and covered here, that the Fed is taking on more than 50 percent of the longer dated Treasuries, and there is only about Ten Billion left on their balance sheet for expansion, and you get the picture of a financial system not cruising into recovery but heading straight at a confrontation with harsh reality.
We have considered the possibility that the Fed is doing this to place exclusively AAA and Treasuries on the balance sheets of the Funds, aka the Shadow Banking System, who are holding some seriously awful garbage. But this does not quite make sense unless those reverse repos are of a very long duration or rolled over automatically for a long period of time. A proper program such as was extended to the banks where the Fed buys the assets outright would be that solution. It made more sense to us that the banking system is still very tight on good capital assets and liquidity.
Here is an update from ZH that is somewhat compelling if one understand the implications. Visualizing the Upcoming Treasury Funding Crisis.
"Summary: foreign purchasers are congregating exclusively around the front end of the Treasury curve, meaning that the primary net purchaser of dated bonds has been the Federal Reserve. As everyone knows by now, the Fed only has $10 billion left out of the $300 billion total allotted for Treasury QE. That should expire next week. ... The time of unravelling may be upon us sooner than most think."Do Tim and Ben = Thelma and Louise?
As the Eagles sang:
"Take it, to the limit, one more time..."
23 February 2009
The Fed's Balance Sheet Strategy to Support Qualitative Easing: A Synopsis
“They [the Fed's financial crisis programs] all make use of the asset side of
the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet. That is, each involves the Fed’s
authorities to extend credit or purchase securities.”
Ben Bernanke, London School of Economics, January 13, 2009
The Fed's strategy is to expand Balance Sheet and to change the mix of the financial assets it holds to stimulate specific troubled markets.
As you will recall, the Fed's Balance Sheet provides the backing for the US Dollar currency among other things, and traditionally has consisted of gold, US Treasury Debt, and the explicitly guaranteed debt of agencies like Ginnie Mae.
What the Fed is doing is expanding the assets on its Balance Sheet, which is quantitative easing, but is doing it by adding specifically targeted non-traditional assets.
The Bernake Fed distinguishes its own approach from the "quantitative easing" of the Bank of Japan. It is an expansion of the central bank's balance sheet, but in the case of the Fed, with a bias. Bernanke calls it 'credit easing' while we prefer to call it 'qualitative easing.'
The Fed is deciding specifically where and to whom to apply its qualitative easing.
This is the controversial part of the program, because the Fed no longer manages the money supply and interest rates, and the general health of the banking system, but targets specific markets and companies for its monetization efforts.
In effect, one might say that the Fed has begun to assume a central planning role for the economy that decides, with specifics, who fails and who survives to succeed. What is troubling in particular is that so far the Fed has retained the perogative to do this without disclosure of the specifics even to Congress.

Bernanke divides the use of balance sheet assets into three groups:
1. lending to financial institutions,
2. providing liquidity to key credit markets, and
3. purchasing longer-term securities.

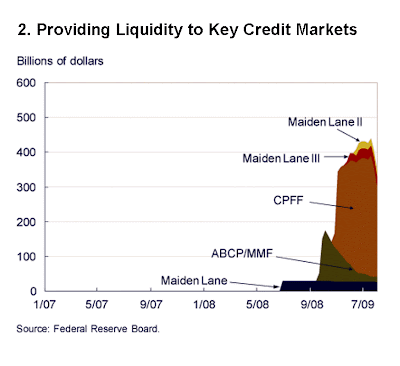

What does "Buying Longer Term Securities" mean? In November 2008, the Federal Reserve announced plans to purchase the direct
obligations of the housing-related government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs),
specifically Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and the Federal Home Loan Banks. In
principle, the extra demand for these obligations is designed to increase the
price of the securities and thereby lower rates paid for mortgages.
Additionally, the Fed outlined plans to purchase mortgage-backed securities
backed by Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and Ginnie Mae. These actions were designed
to improve the availability of credit for the purchase of houses, therefore
supporting the housing markets and financial markets in general.Source: The Federal Reserve
28 January 2009
The Fed Statement
 Good News! The Fed stands ready to buy Treasuries, but not yet so don't worry about monetization. Will they or won't they?
Good News! The Fed stands ready to buy Treasuries, but not yet so don't worry about monetization. Will they or won't they?
Oh by the way:
The Federal Reserve continues to purchase large quantities of agency debt and mortgage-backed securities to provide support to the mortgage and housing markets, and it stands ready to expand the quantity of such purchases and the duration of the purchase program as conditions warrant.
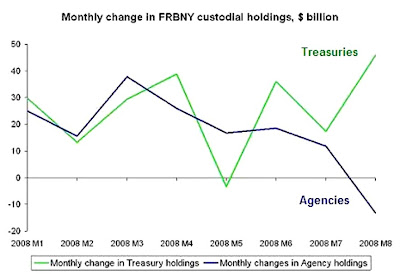
As you may recall, the foreign central banks have been dumping Agency debt en masse and using the proceeds to buy Treasuries, generally in the five to ten year duration of the curve.
So the Fed is buying those Agencies, but not buying Treasuries which would be monetization right? But somehow buying Agency debt is not monetization if it is the foreign central banks who are buying the Treasuries, right?
If the Fed uses its Balance Sheet to buy financial assets at above market prices, essentially providing a subsidy to the holders of those assets, this is not inflationary since that debt already existed, right? Oh, as long as it is at a loss, because as everyone can figure out buying them at 1000 times more than they are worth or marked on the holder's books would surely be inflationary, right? If the Fed buys my stamp collection at 1000 times it true value, that would be inflationary unless they sterilized the transaction. Is the Fed sterilizing all their transactions? Hah!
Will they or won't they indeed. They already are, indirectly. More misdirection from the transparent Fed.
From Tinker, to Evers, to Chance.
Press Release
Release Date: January 28, 2009
For immediate release
The Federal Open Market Committee decided today to keep its target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent. The Committee continues to anticipate that economic conditions are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels of the federal funds rate for some time.
Information received since the Committee met in December suggests that the economy has weakened further. Industrial production, housing starts, and employment have continued to decline steeply, as consumers and businesses have cut back spending. Furthermore, global demand appears to be slowing significantly. Conditions in some financial markets have improved, in part reflecting government efforts to provide liquidity and strengthen financial institutions; nevertheless, credit conditions for households and firms remain extremely tight. The Committee anticipates that a gradual recovery in economic activity will begin later this year, but the downside risks to that outlook are significant.
In light of the declines in the prices of energy and other commodities in recent months and the prospects for considerable economic slack, the Committee expects that inflation pressures will remain subdued in coming quarters. Moreover, the Committee sees some risk that inflation could persist for a time below rates that best foster economic growth and price stability in the longer term.
The Federal Reserve will employ all available tools to promote the resumption of sustainable economic growth and to preserve price stability. The focus of the Committee's policy is to support the functioning of financial markets and stimulate the economy through open market operations and other measures that are likely to keep the size of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet at a high level.
The Federal Reserve continues to purchase large quantities of agency debt and mortgage-backed securities to provide support to the mortgage and housing markets, and it stands ready to expand the quantity of such purchases and the duration of the purchase program as conditions warrant.
The Committee also is prepared to purchase longer-term Treasury securities if evolving circumstances indicate that such transactions would be particularly effective in improving conditions in private credit markets.
The Federal Reserve will be implementing the Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility to facilitate the extension of credit to households and small businesses. The Committee will continue to monitor carefully the size and composition of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet in light of evolving financial market developments and to assess whether expansions of or modifications to lending facilities would serve to further support credit markets and economic activity and help to preserve price stability.
Voting for the FOMC monetary policy action were: Ben S. Bernanke, Chairman; William C. Dudley, Vice Chairman; Elizabeth A. Duke; Charles L. Evans; Donald L. Kohn; Dennis P. Lockhart; Kevin M. Warsh; and Janet L. Yellen. Voting against was Jeffrey M. Lacker, who preferred to expand the monetary base at this time by purchasing U.S. Treasury securities rather than through targeted credit programs.